Chin Augmentation
A well-defined, well-projected chin and jaw- line are crucial to the harmony of a pleasing aesthetically face. When this is not the case, and if the patient is in search of a solution, the anatomic and aesthetic evaluation should be done first. Then the possible treatment modalities can be discussed with the patient.
An anatomic evaluation and facial analysis should be done after taking a complete history. The mandible, the condition of the teeth, occlusion and especially the mentum is thoroughly examined. The analysis of mentum in the vertical, horizontal and transverse plane is done.
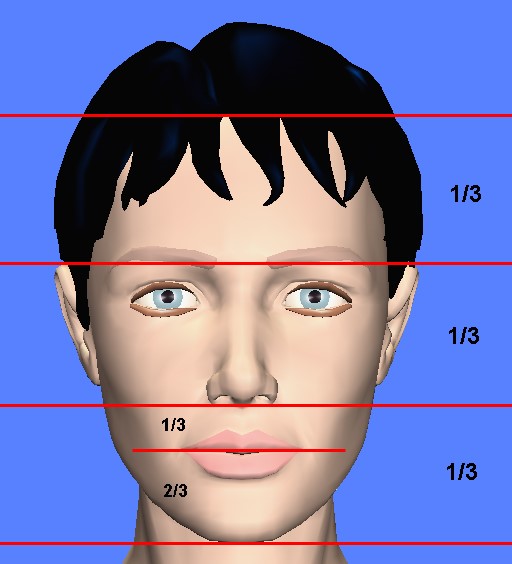
Figure 1: Ideally, on the frontal view the lower face is about one third of the face. The height of the upper lip to the lower lip and chin is 1:2.
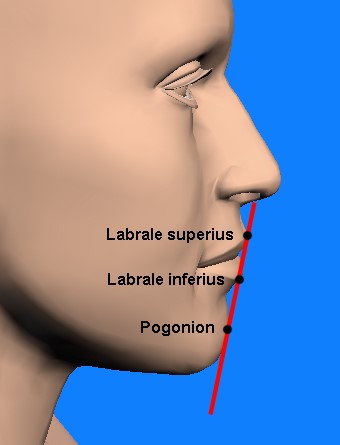
Figure 2: The line passing from the prominent points of the upper and lower lip should ideally touch the anterior-most point of the chin (pogonion) in men. In women the chin may lie up to 2 to 3 mm posterior to this line.
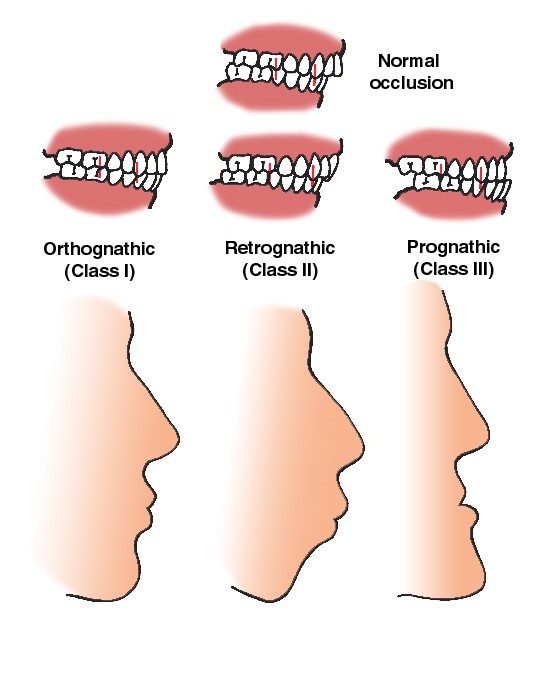
Figure 3: Microgenia is the term for a small chin due to underdevelopment of the body of the mandible while the occlusion (the closure of the upper and lower teeth is normal) is normal.
In micrognathia, both the body and ramus of the mandible are underdeveloped and called as class II malocclusion. The upper teeth is more anterior to the lower teeth (over-bite).
Retrognathia is used for an underdeveloped / malpositioned ramus, with class II malocclusion.
Photographic documentation in frontal, lateral and oblique views should be done. Then computer imaging should be done to show the possible changes to the patient. If the deformity is very severe, detailed radiological examination can be needed. In this situation more complex surgeries can be suggested.
Chin augmentation can be performed with
1. Fillers: This is the easiest modality among these three. It can be done in the office setting under topical anesthesia. Its effect can be usually for a year.
2. Implantation: It is relatively simple and offers permanent results.
3. Osseous genioplasty.

Figure 4: Silicone implant which is anatomically fitting in front of and around the body of the mandible.
Surgical Technique
Chin implantation may be performed through an intraoral or submental approach.
I am more in favor of using a small incision under the chin and then inserting a silicone implant in a pocket opened in front of the body of the mandible. In my experience it gives me the opportunity to be more precise in handling the implant and less risk of infection in comparison to intraoral approach. It can be done under sedation and local anesthesia or under general anesthesia. There will surely be a scar which is barely visible disguised in the submental crease.
Chin implant can be in conjunction with other surgeries such as submental liposuction and/or facelift.
Complications
1. Paresthesia: Altough very rare, it can be due to the damage to the mental nerve.
2. Temporary numbness: It can be the result of edema or implant pressure.
Scar under the chin: Although very difficult to see, there will be a small scar under the chin.



